Skin
Skin is the largest organ in the body, approximately 1.70 sqm surface area, covering the body and protecting it from injury, regulating temperature and preventing us dehydration. Skin has two main layers of cells called the epidermis and the dermis. Epidermis is the outer layer of the skin and contains three main types of cells:
- Squamous cells: flat cells that are packed tightly to make up the top layer
- Basal cells – tall cells that make up the lower layer
- Melanocytes – cells that produce a dark pigment (melanin), the substance that gives skin its colour
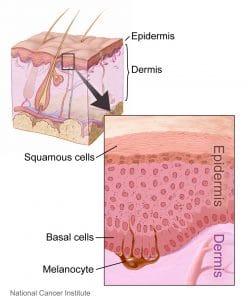



Basal cells multiply and the older cells move upwards in the epidermis. When they flatten out and form a layer they become squamous cells. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make extra melanin to protect the skin from getting burnt. This is what causes skin to tan. Melanocytes are also in non-cancerous (benign) spots on the skin called moles or naevi. Most moles are brown, tan or pink in colour and round in shape.
Dermis is the layer under the epidermis. It contains the roots of hairs, sweat glands, blood and lymph vessels and nerves.


